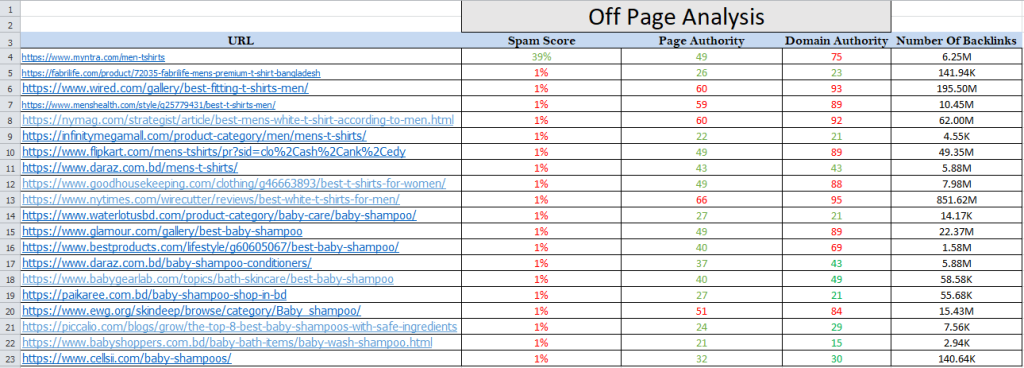
KEYWORD RESEARCH
Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing words and phrases people use in search engines like Google. It helps businesses, bloggers, and marketers understand what their audience is searching for, so they can create content that ranks higher and attracts traffic.
Why Is Keyword Research Important?
SEO Optimization: Helps improve rankings on search engines.
Content Strategy: Guides content creation based on popular search terms.
Traffic Growth: Brings the right audience to your website.
Competitive Advantage: Helps you find gaps in your competitors’ strategies.
How to Do Keyword Research
Brainstorm Seed Keywords
Think of words related to your niche.
Example: If you run a fitness blog, seed keywords could be “weight loss,” “home workouts,” or “healthy diet.”
Use Keyword Research Tools
Free Tools: Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, AnswerThePublic.
Paid Tools: Ahrefs, SEMrush, Ubersuggest, Moz.
Analyze Search Intent
Informational: “How to lose weight fast?” (Blog articles, guides)
Navigational: “Nike official website” (Brand-specific searches)
Transactional: “Buy running shoes online” (People ready to purchase)
Check Keyword Metrics
Search Volume: How many people search for the keyword per month.
Keyword Difficulty (KD): How hard it is to rank for the keyword.
CPC (Cost Per Click): If using for paid ads, higher CPC means higher competition.
Find Long-Tail Keywords
Example: Instead of “best shoes,” target “best running shoes for flat feet.”
Long-tail keywords have less competition but higher conversion rates.
Spy on Competitors
Use tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush to analyze the keywords your competitors rank for.
Look for low-competition, high-potential keywords.
Optimize Your Content
Include keywords in your title, headers, meta description, and content.
Write naturally—don’t stuff keywords!
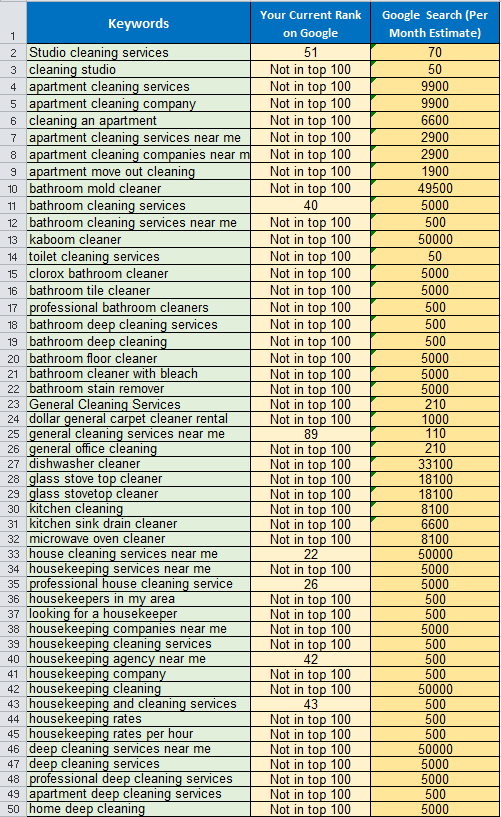
GENERAL ANALYSIS
General Analysis of Keywords
1. Understanding Keywords
Keywords are specific words or phrases that users type into search engines to find information. They are the foundation of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and digital marketing strategies.
2. Types of Keywords
Short-Tail Keywords: (e.g., “shoes”) – High search volume but broad intent.
Long-Tail Keywords: (e.g., “best running shoes for flat feet”) – Lower search volume but higher conversion rates.
Branded Keywords: (e.g., “Nike running shoes”) – Specific to a brand.
Competitor Keywords: (e.g., “Adidas vs Nike shoes”) – Used for competitive analysis.
Transactional Keywords: (e.g., “buy sneakers online”) – Indicate purchase intent.
Informational Keywords: (e.g., “how to clean white sneakers”) – Used for educational content.
3. Keyword Metrics for Analysis
Search Volume: Measures how often a keyword is searched monthly.
Keyword Difficulty (KD): Indicates how hard it is to rank for a keyword.
Cost Per Click (CPC): The cost of paid ads for the keyword.
Search Intent: Determines whether the keyword is informational, navigational, or transactional.
4. Competitive Analysis
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Ubersuggest to analyze keyword competition.
Identify low-competition, high-value keywords to target.
Monitor competitor rankings and discover keyword gaps.
5. Importance of Keyword Optimization
Improves SEO rankings and website visibility.
Increases organic traffic and engagement.
Enhances content relevance and user experience
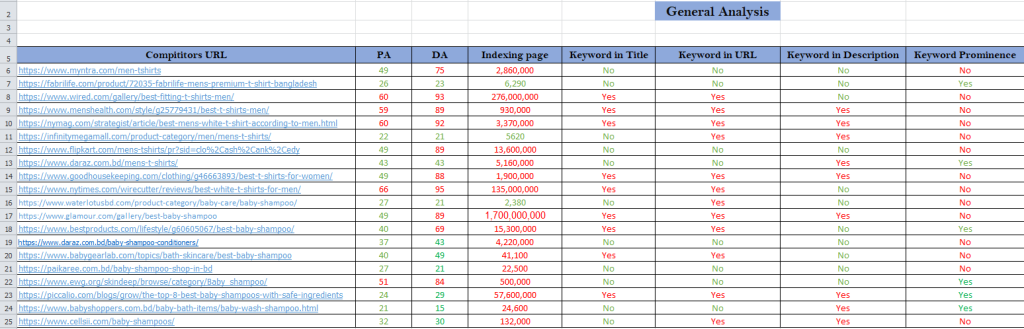
ON PAGE ANALYSIS
On-Page Analysis
On-page analysis refers to the evaluation of factors within a webpage that affect its search engine rankings. This includes content, HTML elements, and site architecture.
1. Key Elements of On-Page SEO Analysis
A. Content Optimization
Keyword Placement: Ensure target keywords appear naturally in the title, headers, and body text.
Content Quality: Content should be original, informative, and engaging for users.
Readability: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings for better readability.
Multimedia Usage: Include images, videos, and infographics to enhance user experience.
Internal Linking: Link to related pages to improve navigation and SEO structure.
B. HTML & Meta Tags Optimization
Title Tag: Should be under 60 characters and contain the main keyword.
Meta Description: Should be under 160 characters with a compelling CTA.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.): Use headings to structure content properly.
Alt Text for Images: Helps search engines understand image content.
URL Structure: Use short, descriptive URLs (e.g.,
example.com/on-page-seo-tips).
C. User Experience (UX) Factors
Page Speed: Optimize loading time for better user retention.
Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure the site is responsive on all devices.
Navigation & Structure: A well-organized website improves usability.
D. Technical SEO Checks
Canonical Tags: Prevent duplicate content issues.
Schema Markup: Helps search engines understand page content better.
Robots.txt & Sitemap: Ensure proper indexing by search engines.
2. Tools for On-Page Analysis
Google Search Console – Identifies indexing and performance issues.
Google PageSpeed Insights – Checks page speed and suggests improvements.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider – Analyzes on-page elements in bulk.
Yoast SEO (WordPress Plugin) – Provides on-page SEO suggestions.
3. Benefits of On-Page Optimization
✅ Higher search engine rankings
✅ Better user experience
✅ Increased organic traffic
✅ Higher conversion rates
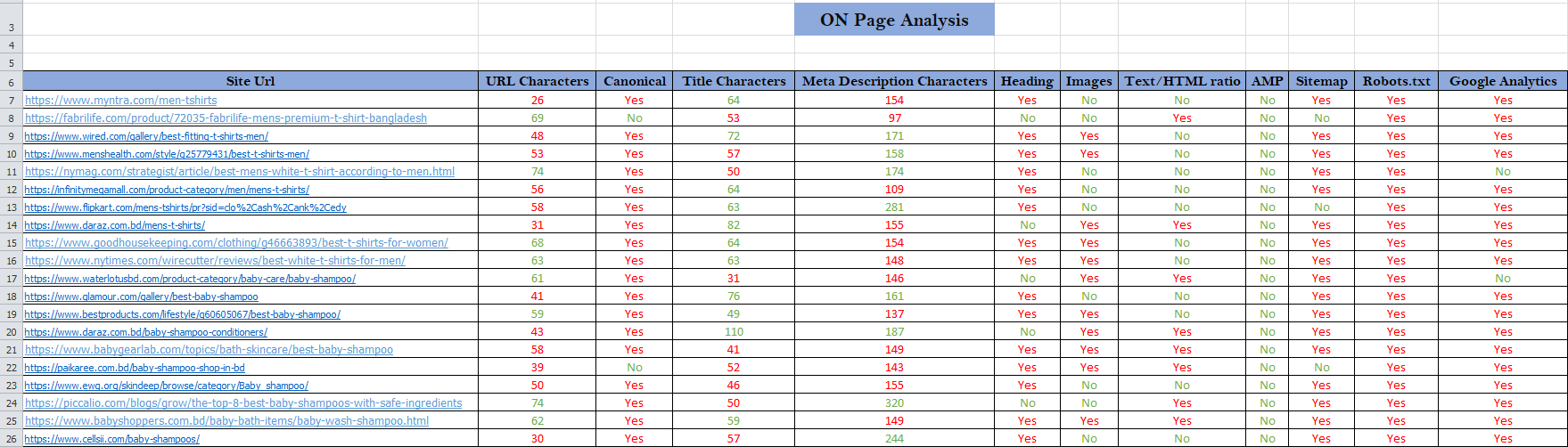
OFF PAGE ANALYSIS
Off-Page SEO Analysis
Off-page SEO refers to all the activities performed outside of a website to improve its search engine rankings. It primarily focuses on building authority, credibility, and trustworthiness through backlinks, social signals, and brand mentions. Here’s a detailed breakdown of an off-page SEO analysis:
1. Backlink Profile Analysis
Total Backlinks: Assess the total number of backlinks pointing to the website.
Quality of Links: Check if the backlinks are from authoritative, relevant, and high-DA (Domain Authority) websites.
Anchor Text Distribution: Ensure a natural mix of branded, generic, and keyword-rich anchor texts.
Dofollow vs. Nofollow Ratio: A healthy backlink profile should have a mix of both types of links.
Toxic Links Detection: Identify spammy or low-quality links that could harm SEO and consider disavowing them.
2. Competitor Backlink Analysis
Compare Link Profiles: Identify competitor backlinks and analyze opportunities for acquiring similar high-quality links.
Broken Link Building: Find broken links on authoritative sites and suggest your content as a replacement.
Guest Posting & Outreach: Discover where competitors are guest posting and reach out for collaborations.
3. Brand Mentions & Citations
Unlinked Brand Mentions: Identify online mentions of the brand without a backlink and request a link.
NAP Consistency: Ensure Name, Address, and Phone Number (NAP) consistency across business directories.
Local Citations: Optimize local business listings on platforms like Google My Business, Yelp, and industry-specific directories.
4. Social Media Signals
Engagement Metrics: Check shares, likes, and comments on social media platforms.
Influencer Collaborations: Partner with influencers to enhance brand visibility and acquire backlinks.
Content Virality: Analyze which content pieces are gaining traction and replicate successful strategies.
5. Online Reputation Management
Customer Reviews: Monitor and respond to customer reviews on Google, Trustpilot, and other review platforms.
Forum & Community Engagement: Participate in niche forums, Quora, and Reddit to establish authority.
Press & PR Mentions: Leverage digital PR to get featured in news sites and authoritative publications.
6. Technical & Performance Off-Page Factors
Page Load Speed: Ensure fast loading times to prevent high bounce rates.
Mobile-Friendliness: A mobile-responsive site improves user experience and rankings.
Indexation & Crawlability: Verify that backlinks are indexed by search engines for SEO impact.
Final Thoughts
Off-page SEO is crucial for building a strong online presence. By continuously monitoring backlinks, social signals, and brand reputation, a website can improve its authority and rank higher in search engine results.